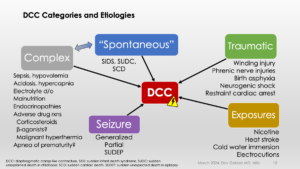
Novel diaphragmatic cramp-like contracture (DCC) appears to have numerous causes. The endpoint is the same for all: diaphragm cramp > effective bilateral diaphragm paralysis > respiratory arrest. This might explain SIDS. It is preceded by diaphragm fatigue. DCC categories include “spontaneous” (those in sleeping children), traumatic (winding injuries), exposures (e.g. nicotine toxicity, electrocutions and cold water immersions), seizures (both generalized and partial/focal) and finally, “complex” (relating to medical illnesses and medication side effects).